Modern GFCI outlets can self-test to ensure they’re working correctly. Usually, when a GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlet is blinking red, something needs your attention.
However, the LED indicator light on a GFCI outlet has several possible statuses. A GFCI outlet blinking red will have a very different meaning than an outlet flashing yellow. Most homeowners don’t know how to troubleshoot it on their own.
So, if one of your GFCI garage outlets is flashing red or yellow, this article will help you find the cause.
Why Do GFCI Outlets Have Status Lights?
Beginning in 2015, all new installations of GFCI outlets and circuit breakers must be auto-monitoring.
This means the outlets must conduct regular internal tests to ensure they activate correctly during a ground fault event.
If the self-test function detects an error, the GFCI outlet must immediately trip, opening the circuit and cutting off the outlet’s power. It must also provide an audible warning or a visual indication with the status light.
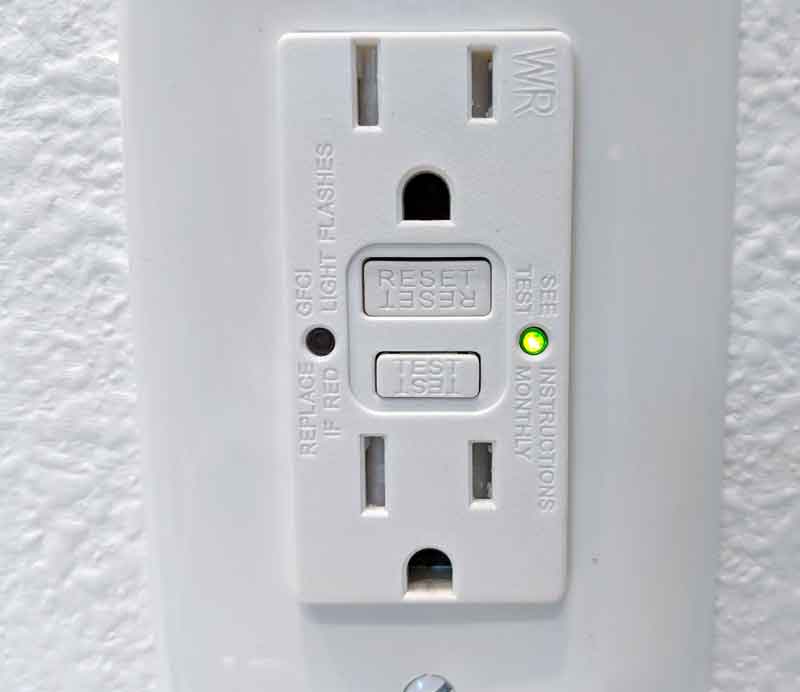
While a GFCI outlet may look like a conventional three-pin outlet, it also has test and reset buttons.
An indicator light will also be visible next to the reset and test button on the front panel.
The indicator light will show the following statuses.
- Off (no light)
- Green (solid)
- Red (flashing or solid)
- Yellow (flashing or solid)
Let’s dive into what each of these status lights means.
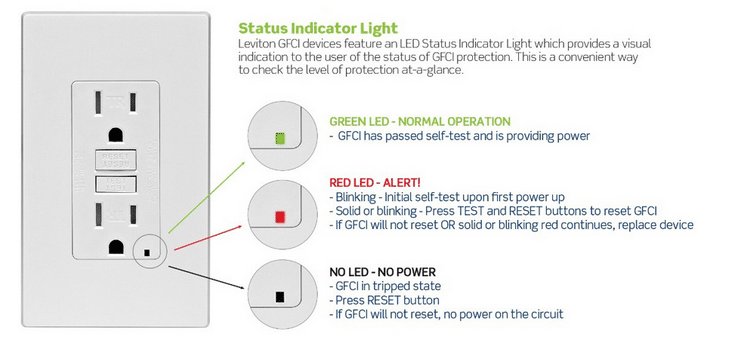
GFCI Indicator Light Is Off
If the indicator light is off, no power is running to the outlet. This usually means the breaker has been tripped. Check your breaker box to restore power.
GFCI Indicator Light Is Green
A green light on the GFCI outlet indicates that it has passed the automated self-test, is providing power, and is working correctly.
GFCI Indicator Light Is Red (Solid or Flashing)
For GFCI outlets with only one status indicator light, a red light means that it has failed a self-test and has a problem somewhere.
If the GFCI device starts blinking under normal circumstances, it has been tripped.
The most common reasons you see a red light on your GFCI outlet are:
- There’s a fault in the wiring of the circuit.
- A ground fault has occurred.
- An overloaded circuit.
- Another GFCI outlet on the circuit has tripped. This can sometimes cause nearby GFCI outlets to trip as well.
- The GFCI outlet is defective. Replace it immediately.
- The GFCI outlet has reached the end of its useful lifespan. Replace it immediately.
It’s a common misconception that there’s a difference between a GFCI outlet blinking red light or a solid red light. This is not accurate. Major manufacturers like Lutron, Leviton, and Legrand all state that a solid or flashing red light on a GFCI outlet signifies a faulty system. Have this examined by a professional electrician as soon as possible.
Depending on the particular GFCI outlet model, the same manufacturer can use a solid or flashing red light. It’s simply a design preference and doesn’t carry any additional meaning.
Some manufacturers, like Eaton, use both a red and a yellow status indicator light. We’ll look at that particular case in the next section.
GFCI Indicator Light Is Yellow (Solid Or Flashing)
Some Eaton GFCI outlets have red and yellow (amber) indicator lights.
On these models, the red light indicates that the GFCI outlet has degraded and no longer provides protection. Replace these outlets as soon as possible.
On these units, the GFCI outlet yellow light means the outlet failed a self-test.
How to Self-Test your GFCI Outlet
When you have a red light on your GFCI outlet (or yellow on some brands), the first step is to perform a self-test.
A simple reset will usually cause the outlet to function normally again.
Start by unplugging all devices from the GFCI circuit except for a small lamp or radio (powered off). These devices draw minimal power from the circuit. We’ll use them to verify that power is (or is not) flowing through the circuit.
Start by verifying that the breaker for this outlet has not been tripped at your service panel.
Next, press the TEST button on your GFCI outlet.
If the status indicator light turns green, the fault was caused by the device (or devices) plugged into the circuit. This is especially common in bathrooms or using extension cables or power strips.
If the GFCI will not reset, this means one of two things. Either the outlet needs to be replaced, or the Line and Load wires are reversed on the back of the outlet.
As irritating as this may be, the GFCI outlet has done its job, preventing possible damage.
Perform a self-test by pressing the TEST button followed by the RESET button every month to ensure proper operation.
Additionally, when the outlet receives power, it will blink while performing a self-test. You can also test the GFCI outlet manually by pressing the “TEST” and “RESET” buttons.

Where Are GFCI Outlets Required?
Building codes have required GFCI outlets in homes and businesses since 1973. This has helped reduce electrical accidents by 83%.
Over the years, the building code has expanded the number of locations where GFCI outlets are required.
Currently, the national code requires GFCI installations in the following home areas:
- Any outlets installed on the outside of the house.
- Any electrical outlets installed in a bathroom.
- All outlets installed in a garage must be GFCI.
- Every outlet on a kitchen countertop must be a GFCI-equipped unit.
- Any kitchen outlet installed within six feet of a kitchen sink.
- At least one GFCI outlet is required in the basement.
- Any crawl spaces.
- To power any devices in a wet bar.
- To supply power to electrically heated floors
How Does A GFCI Outlet Work?
GFCI stands for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter.
A GFCI outlet acts as a localized circuit breaker at the outlet, containing a sensor that constantly monitors the electrical current.
Under normal conditions, electrical current flows regularly and steadily through circuit wiring. When the current experiences a ground fault, it surges as it jumps to the new ground (possibly a human body).
The GFCI can detect surges as low as four or six milliamps (0.0004 amps or 0.0006 amps).
The instant (less than 1/10th of a second) it detects the surge caused by a ground fault, it will open the circuit and, therefore, cut off the flow of electricity.
If the current in one of the wires changes (generally a reduction in the neutral circuit), a small amount of current is induced in the GFCI coil. This immediately trips (opens) the primary circuit, preventing current from flowing and shutting down the appliance.
An example is someone using a hair dryer next to a sink filled with water. If the hairdryer fell into the water while the circuit was live, the current would ground through the person’s body, electrocuting them.
However, a GFCI outlet would trip the circuit, cutting off the current flow to protect the user. The person may still receive an electrical shock. However, the chance of serious injury would be significantly reduced.
Wrapping It Up
Depending on the manufacturer and model, GFCI outlets have several different status indicator lights.
These are:
- Off (no light): No power to the outlet.
- Green (solid): The outlet is functioning normally.
- Red (flashing or solid): A solid or flashing red light on GFCI outlets indicate a fault in the system. This may also suggest to replace the outlet.
- Yellow (flashing or solid): This means a fault in the system.
Most manufacturers design GFCI outlets to last up to twenty-five years. Replace the GFCI garage outlet if the indicator light remains red or yellow after a self-test and reset.
